

Under some natural restrictions on the boundary values this solution is constructed as the limit with respect to a small parameter of a sequence of solutions to Dirichlet problems for an elliptic differential equation. delta S delta Q / T During a thermodynamic process, the temperature T of an object changes as heat Q is applied or extracted. We prove that the first boundary value problem for a second order forward-backward parabolic differential equation in a bounded domain $G_T\subset\mathbb$, where $d\geqslant2$, has a unique entropy solution in the sense of F. Otto. This article is cited in 4 scientific papers (total in 4 papers)Įntropy solutions to a second order forward-backward parabolic differential equation Then look up the ∆S values of the reactants SO 2 (g) and O 2 (g) and plug it into the equation.Sibirsk. If there is a coefficient in front of the substance then you must multiply the substance’s value of ∆S with the coefficient. Plug the value into the equation such that: The potentials identified in this construction depend on. Mass, energy, entropy, and exergy balance equations are applied to each. When G 0 the reaction (or a process) is at equilibrium.
#Entropy equation free#
G (Change in Gibbs Energy) of a reaction or a process indicates whether or not that the reaction occurs spontaniously. Thermal cracking is an example of a reaction whose energetic are dominated by entropy (S) rather than by enthalpy (H) in the Gibbs Free Energy equation.
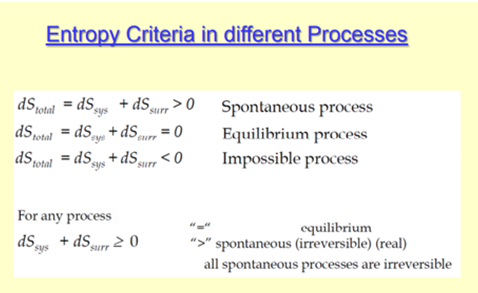
Also, scientists have concluded that in a spontaneous process the entropy of process must increase. Moreover, the entropy of solid (particle are closely packed) is more in comparison to the gas (particles are free to move). The above equation is one of the most widely used equation in thermodynamics. Entropy is a thermodynamic function that we use to measure uncertainty or disorder of a system.

We point out that for the implementation of PT symmetry, the symmetrical canonical form of the Heun equation is more suitable than its non-symmetrical canonical form. Regarding the entropy balance equation (EnBE) for a closed system shown in Fig. Gibbs Free Energy Change, Entropy Change & Enthalpy Change Calculator. Look up the value of ∆S of SO 3 (g), the product, on the chart. We derive exactly solvable potentials from the formal solutions of the confluent Heun equation and determine conditions under which the potentials possess PT symmetry.

Classify them either as the reactant(s) or product(s).Ģ(∆S value SO 3 (g)) – Write out the equation with the substances in them. These values are then put into the equation: If these values are not known, then you can use the ∆S values of the substances in the chemical reaction usually given to you in a chart. Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Which can be manipulated into ∆S= ∆H-∆G/T The Fundamental Equations of Change in Statistical Ensembles and Biological Populations. This version makes the connection between a. where k B is Boltzmanns constant ( 1.38 × 10 23 J / K 0.86 × 10 4 e V / K) and W A is the number of microstates corresponding to the macrostate A. One way is by using the known values of ∆H, ∆G, and the temperature of the system and plugging these values in the equation: The microscopic way to calculate the entropy of a system that is in a macrostate A is given by the equation. This reaction shows that to form 1 M of liquid water, 286 kJ heat evolves. Lazare Carnot, a French mathematician suggested in his 1803 paper named Fundamental Principles of Equilibrium. There are several ways to calculate entropy. in equations has to be there on the left-hand side. An Entropy contains a broad range of properties of a thermodynamic system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
